The stock market serves as a dynamic platform where investors can buy and sell shares of publicly traded companies. It is a complex ecosystem that reflects the economic health of a nation and provides opportunities for wealth creation. Investing in the stock market is not merely about purchasing stocks; it involves understanding market dynamics, analyzing trends, and making informed decisions based on various factors.
The allure of potentially high returns attracts both seasoned investors and novices alike, but it is essential to approach this venture with a well-informed mindset. Historically, the stock market has been a significant driver of wealth accumulation. For instance, the S&P 500 index, which tracks the performance of 500 large companies in the U.S., has delivered an average annual return of about 10% over the long term.
This statistic underscores the potential for growth that exists within the market. However, it is crucial to recognize that investing in stocks also comes with inherent risks. Market fluctuations can lead to substantial losses, making it imperative for investors to educate themselves about the various aspects of stock market investing before diving in.
Key Takeaways
- Stock market investing requires understanding market dynamics and investment principles.
- Analyzing market trends and using both fundamental and technical analysis are crucial for informed decisions.
- Effective risk management and portfolio diversification help minimize potential losses.
- Options and futures trading offer advanced opportunities but require specialized knowledge.
- Utilizing online tools and developing a solid trading strategy enhance trading success.
Understanding Market Analysis and Trends
Market analysis is a critical component of successful investing, as it involves evaluating various factors that influence stock prices. Investors typically engage in two primary types of analysis: fundamental analysis and technical analysis. Fundamental analysis focuses on evaluating a company’s financial health, including its earnings, revenue growth, and overall economic conditions.
By examining these factors, investors can gauge whether a stock is undervalued or overvalued relative to its intrinsic value. On the other hand, technical analysis relies on historical price movements and trading volumes to predict future price trends. This approach utilizes charts and various indicators to identify patterns that may suggest future market behavior.
For example, moving averages can help investors determine the overall trend direction, while momentum indicators can signal potential reversals. Understanding these analytical methods allows investors to make more informed decisions and better navigate the complexities of the stock market.
Risk Management and Portfolio Diversification
Risk management is an essential aspect of investing that aims to minimize potential losses while maximizing returns. One of the most effective strategies for managing risk is portfolio diversification. By spreading investments across various asset classes, sectors, and geographic regions, investors can reduce their exposure to any single investment’s volatility.
For instance, a well-diversified portfolio might include stocks from different industries, bonds, real estate investment trusts (REITs), and commodities. The rationale behind diversification lies in the principle that not all investments will perform poorly at the same time. During economic downturns, certain sectors may suffer while others thrive.
For example, during a recession, consumer staples companies often perform better than luxury goods manufacturers. By holding a mix of assets, investors can cushion their portfolios against market fluctuations and enhance their chances of achieving consistent returns over time.
Fundamental and Technical Analysis
| Analysis Type | Key Metrics | Description | Purpose | Time Horizon |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fundamental Analysis | Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio | Measures company’s current share price relative to its per-share earnings | Evaluate intrinsic value and company profitability | Long-term |
| Fundamental Analysis | Debt-to-Equity Ratio | Indicates the relative proportion of shareholders’ equity and debt used to finance assets | Assess financial leverage and risk | Long-term |
| Fundamental Analysis | Return on Equity (ROE) | Measures profitability by revealing how much profit a company generates with shareholders’ equity | Evaluate management effectiveness | Long-term |
| Technical Analysis | Moving Averages (MA) | Smooths price data to identify trends over a specific period | Identify trend direction and potential support/resistance | Short to Medium-term |
| Technical Analysis | Relative Strength Index (RSI) | Measures speed and change of price movements to identify overbought or oversold conditions | Signal potential trend reversals | Short-term |
| Technical Analysis | MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) | Shows relationship between two moving averages of a security’s price | Identify momentum changes and trend direction | Short to Medium-term |
Fundamental analysis delves into a company’s financial statements, management team, competitive advantages, and market position to assess its overall value. Investors scrutinize metrics such as earnings per share (EPS), price-to-earnings (P/E) ratios, and return on equity (ROE) to determine whether a stock is worth buying or selling. For instance, if a company has a low P/E ratio compared to its industry peers, it may indicate that the stock is undervalued and could be a good investment opportunity.
Conversely, technical analysis focuses on price movements and trading volumes to forecast future price trends. Traders often use charts to identify patterns such as head-and-shoulders or double tops that may signal potential reversals or continuations in price movements. Indicators like Relative Strength Index (RSI) or Bollinger Bands can provide insights into whether a stock is overbought or oversold.
By combining both fundamental and technical analysis, investors can develop a more comprehensive understanding of market dynamics and make informed trading decisions.
Introduction to Options and Futures Trading
Options and futures are derivative instruments that provide investors with unique opportunities to profit from price movements without directly owning the underlying assets. Options give investors the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price within a specified timeframe. This flexibility allows traders to hedge against potential losses or speculate on price movements with limited risk.
Futures contracts, on the other hand, obligate investors to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price on a specific date in the future. These contracts are commonly used in commodities trading but have also gained popularity in financial markets for hedging purposes. For example, a farmer may use futures contracts to lock in prices for their crops before harvest, protecting themselves from potential price declines.
Understanding how these instruments work can enhance an investor’s toolkit and provide additional avenues for profit generation.
Building a Successful Trading Strategy
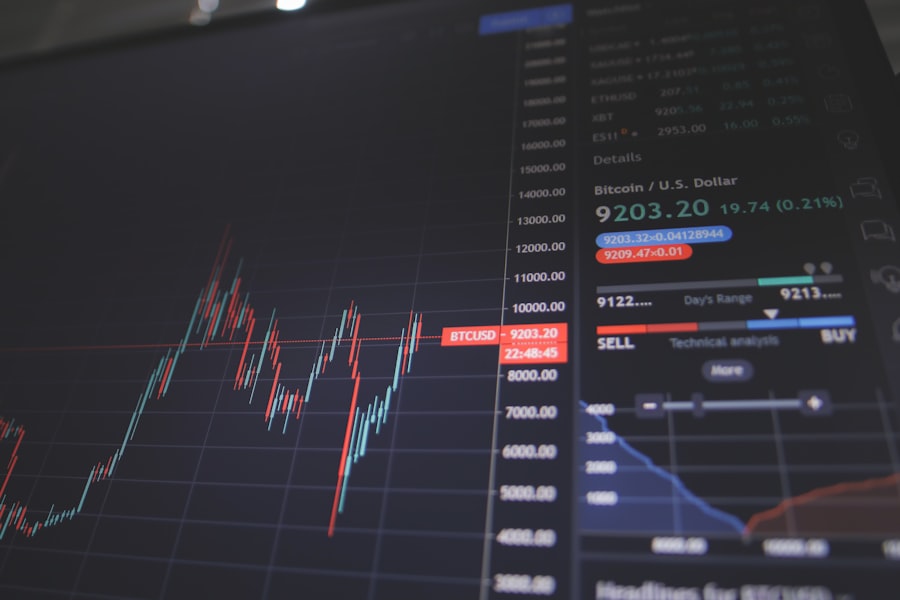

Creating a successful trading strategy requires careful planning and consideration of various factors that influence market behavior. A well-defined strategy should outline specific goals, risk tolerance levels, and entry and exit points for trades. For instance, an investor might adopt a momentum trading strategy that focuses on stocks exhibiting strong upward trends while setting predefined stop-loss orders to limit potential losses.
Additionally, backtesting is an essential component of developing a trading strategy. This process involves applying the strategy to historical data to evaluate its effectiveness over time. By analyzing past performance, traders can identify strengths and weaknesses in their approach and make necessary adjustments before deploying real capital in live markets.
A disciplined approach to strategy development can significantly enhance an investor’s chances of success in the stock market.
Using Online Tools and Platforms for Trading
The advent of technology has revolutionized stock market investing by providing investors with access to sophisticated online tools and platforms. These platforms offer various features such as real-time market data, advanced charting capabilities, and research resources that empower investors to make informed decisions. For example, platforms like TD Ameritrade or E*TRADE provide users with comprehensive educational materials alongside their trading interfaces.
Moreover, mobile trading applications have made it easier for investors to manage their portfolios on the go. With just a few taps on their smartphones, traders can execute trades, monitor market conditions, and receive alerts about significant price movements. The convenience offered by these online tools has democratized access to financial markets, allowing individuals from diverse backgrounds to participate in stock trading with greater ease than ever before.
Advanced Trading Techniques and Strategies
As investors gain experience in the stock market, they may seek to explore advanced trading techniques that can enhance their profitability. One such technique is algorithmic trading, which involves using computer algorithms to execute trades based on predefined criteria. This method allows traders to capitalize on market inefficiencies at speeds unattainable by human traders.
Another advanced strategy is options trading strategies such as straddles or strangles, which involve buying both call and put options simultaneously to profit from significant price movements in either direction. These strategies require a deep understanding of options pricing models and volatility assessments but can yield substantial returns when executed correctly. Additionally, employing risk-reward ratios can help traders assess potential trade setups more effectively.
By calculating the potential profit against the possible loss for each trade, investors can make more informed decisions about which trades align with their risk tolerance levels. In conclusion, navigating the complexities of stock market investing requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses understanding market analysis, risk management strategies, analytical techniques, and advanced trading methods. By leveraging these concepts effectively, investors can position themselves for success in an ever-evolving financial landscape.