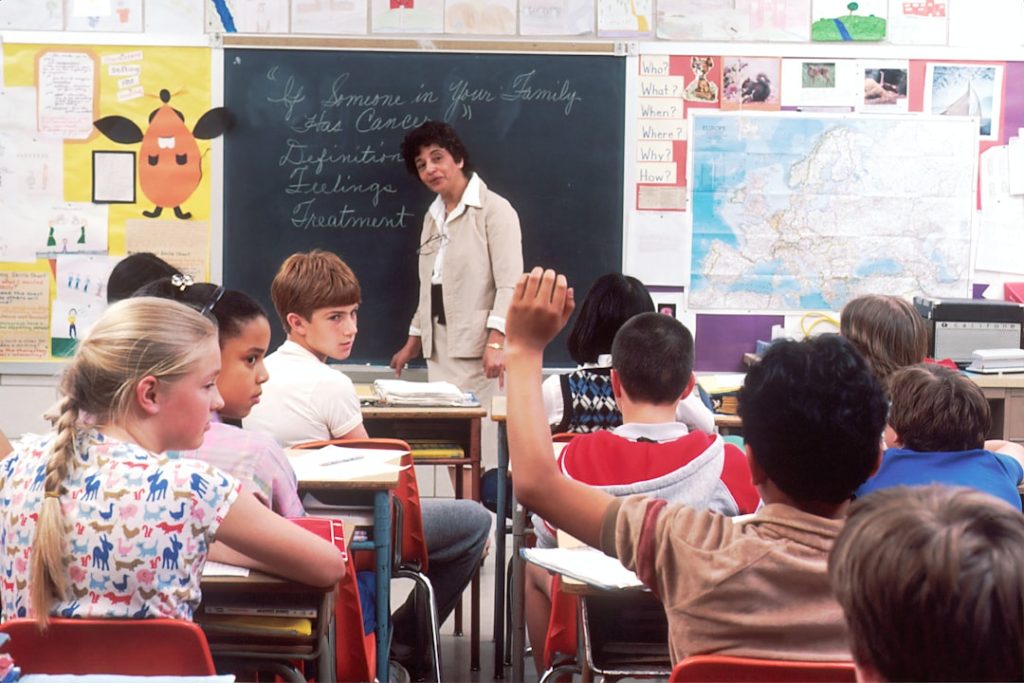
Student engagement is a multifaceted concept that encompasses the emotional, cognitive, and behavioral dimensions of a learner’s experience in the educational environment. Emotional engagement refers to the feelings students have towards their learning experiences, which can significantly influence their motivation and willingness to participate. Cognitive engagement involves the mental effort students invest in their learning, including their ability to think critically and apply knowledge.
Behavioral engagement is observable through students’ participation in class activities, attendance, and overall involvement in the learning process. Understanding these dimensions is crucial for educators aiming to create an environment where students are not only present but actively involved in their education. To foster student engagement, educators must recognize the diverse backgrounds and experiences that each student brings to the classroom.
This recognition allows teachers to tailor their approaches to meet the unique needs of their students. For instance, incorporating culturally relevant materials can resonate with students’ identities and experiences, thereby enhancing emotional engagement. Additionally, providing opportunities for students to take ownership of their learning—such as through choice in assignments or projects—can lead to increased cognitive and behavioral engagement.
By understanding the various facets of student engagement, educators can implement strategies that promote a more dynamic and interactive learning environment.
Key Takeaways
- Student engagement is crucial for effective learning and can be enhanced through active participation and interest.
- Creating a positive classroom environment supports student motivation and collaboration.
- Differentiated instruction addresses diverse learning needs by tailoring teaching methods and materials.
- Integrating technology can enrich lessons and facilitate interactive learning experiences.
- Encouraging student-centered and project-based learning promotes autonomy, critical thinking, and real-world application.
Building a Positive Classroom Environment
Creating a positive classroom environment is foundational to fostering student engagement and success. A supportive atmosphere encourages students to express themselves freely, take risks in their learning, and collaborate with peers. Establishing clear expectations for behavior and academic performance is essential; however, it is equally important to cultivate a sense of community within the classroom.
This can be achieved through team-building activities, collaborative projects, and open discussions that allow students to share their thoughts and feelings. When students feel safe and valued, they are more likely to engage actively in their learning. Moreover, the physical layout of the classroom can significantly impact the overall environment.
Flexible seating arrangements that allow for group work and discussions can promote collaboration and interaction among students. Incorporating elements such as plants, artwork, or student-created displays can also enhance the aesthetic appeal of the classroom, making it a more inviting space. Teachers should strive to create an environment that reflects inclusivity and respect for diversity, where every student feels represented and heard.
By prioritizing a positive classroom environment, educators lay the groundwork for enhanced student engagement and academic achievement.
Utilizing Differentiated Instruction
Differentiated instruction is an approach that recognizes the diverse learning needs of students and tailors teaching methods accordingly. This strategy involves modifying content, processes, products, or learning environments based on individual student readiness, interests, and learning profiles. For example, in a mixed-ability classroom, a teacher might provide advanced reading materials for gifted students while offering additional support and scaffolding for those who struggle with comprehension.
This approach not only addresses varying academic levels but also fosters a sense of belonging among all learners. Incorporating differentiated instruction requires ongoing assessment and reflection on student progress. Teachers can utilize formative assessments—such as quizzes, observations, or student reflections—to gauge understanding and adjust instruction as needed.
Additionally, offering choices in how students demonstrate their learning can enhance motivation and engagement. For instance, allowing students to choose between a written report, a presentation, or a creative project enables them to leverage their strengths while still meeting learning objectives. By embracing differentiated instruction, educators can create a more inclusive classroom that meets the needs of all learners.
Incorporating Technology in the Classroom
| Metric | Description | Value | Source/Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Percentage of Schools Using Technology | Proportion of schools that have integrated technology tools in classrooms | 85% | National Ed Tech Survey, 2023 |
| Average Student-to-Device Ratio | Number of students per digital device available in classrooms | 3:1 | EdTech Analytics, 2023 |
| Teacher Training on Technology | Percentage of teachers who received formal training on classroom technology use | 72% | Teacher Professional Development Report, 2023 |
| Improvement in Student Engagement | Increase in student engagement levels after technology integration | 30% increase | Classroom Impact Study, 2022 |
| Use of Interactive Whiteboards | Percentage of classrooms equipped with interactive whiteboards | 65% | School Infrastructure Report, 2023 |
| Access to Online Learning Platforms | Percentage of students with access to online educational resources | 90% | Digital Learning Access Survey, 2023 |
| Increase in Test Scores | Average improvement in standardized test scores attributed to technology use | 12% improvement | Education Outcomes Report, 2023 |
The integration of technology in education has transformed traditional teaching methods and opened new avenues for student engagement. Digital tools such as interactive whiteboards, educational apps, and online collaboration platforms can enhance the learning experience by making it more interactive and accessible. For instance, using platforms like Google Classroom allows teachers to streamline communication, distribute resources efficiently, and facilitate collaborative projects among students.
This not only saves time but also encourages students to take an active role in their learning process. Moreover, technology can provide personalized learning experiences that cater to individual student needs. Adaptive learning software can assess a student’s proficiency level and adjust the difficulty of tasks accordingly, ensuring that each learner is challenged appropriately.
Additionally, incorporating multimedia resources—such as videos, podcasts, or virtual simulations—can cater to various learning styles and keep students engaged. However, it is essential for educators to strike a balance between technology use and traditional teaching methods to ensure that technology enhances rather than detracts from the learning experience.
Encouraging Student-Centered Learning
Student-centered learning shifts the focus from teacher-led instruction to an approach where students take an active role in their education. This pedagogical shift encourages learners to explore topics of interest, ask questions, and engage in discussions that deepen their understanding. By fostering an environment where students feel empowered to direct their own learning journeys, educators can cultivate critical thinking skills and intrinsic motivation.
For example, project-based learning initiatives allow students to investigate real-world problems while collaborating with peers and applying their knowledge in meaningful ways. In practice, encouraging student-centered learning involves providing opportunities for choice and autonomy within the curriculum. Teachers can facilitate this by allowing students to select topics for research projects or choose how they wish to demonstrate their understanding of a concept.
Additionally, incorporating inquiry-based learning strategies—where students pose questions and seek answers through exploration—can further enhance engagement. By prioritizing student-centered approaches, educators not only promote active participation but also help students develop essential skills for lifelong learning.
Implementing Project-Based Learning

Project-based learning (PBL) is an instructional method that engages students in exploring real-world problems through hands-on projects over an extended period. This approach encourages collaboration among students as they work together to investigate complex issues and develop solutions. For instance, a science class might undertake a project where they design sustainable energy solutions for their school or community.
Such projects not only deepen content knowledge but also foster critical thinking, creativity, and teamwork skills. The implementation of PBL requires careful planning and scaffolding by educators to ensure that students remain focused and productive throughout the project timeline. Teachers must provide clear guidelines while allowing flexibility for student input and creativity.
Regular check-ins and feedback sessions can help keep students on track while also encouraging reflection on their learning process. By integrating PBL into the curriculum, educators create opportunities for authentic learning experiences that resonate with students’ interests and aspirations.
Providing Constructive Feedback
Constructive feedback is a vital component of the learning process that helps students understand their strengths and areas for improvement. Effective feedback should be specific, timely, and actionable; it should guide students toward achieving their academic goals while fostering a growth mindset. For example, instead of simply marking an assignment as incorrect, a teacher might provide comments that highlight what was done well while also suggesting specific strategies for improvement.
This approach not only clarifies expectations but also encourages students to view challenges as opportunities for growth. In addition to written feedback on assignments, verbal feedback during class discussions or one-on-one conferences can be incredibly impactful. Engaging in dialogue about a student’s work allows for immediate clarification of misunderstandings and reinforces positive behaviors.
Furthermore, encouraging peer feedback can foster a collaborative classroom culture where students learn from one another’s perspectives. By prioritizing constructive feedback practices, educators empower students to take ownership of their learning journey while promoting continuous improvement.
Fostering a Growth Mindset
Fostering a growth mindset within the classroom is essential for encouraging resilience and perseverance among students. A growth mindset—the belief that abilities can be developed through dedication and hard work—contrasts with a fixed mindset, which views intelligence as static. Educators play a crucial role in shaping students’ mindsets by emphasizing effort over innate ability and celebrating progress rather than solely focusing on outcomes.
For instance, praising a student’s persistence in tackling challenging problems reinforces the idea that struggle is a natural part of the learning process. To cultivate a growth mindset culture, teachers can incorporate activities that promote reflection on personal growth and goal-setting. Encouraging students to set specific academic goals and track their progress fosters accountability while reinforcing the idea that improvement is achievable through effort.
Additionally, sharing stories of famous individuals who overcame obstacles through perseverance can inspire students to adopt a similar outlook on challenges they face in their own lives. By embedding growth mindset principles into daily practices, educators create an environment where students feel empowered to embrace challenges as opportunities for development rather than threats to their self-worth.



